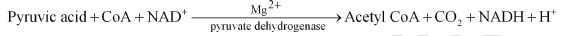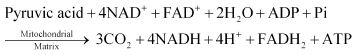Chapter 14 : Respiration in Plants

Cellular Respiration
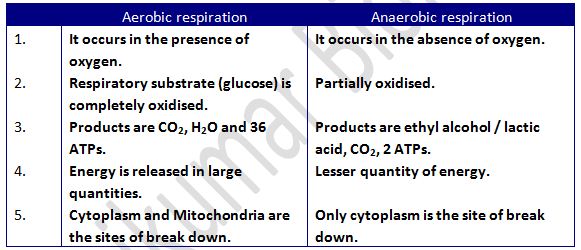
Types of respiration:
· Aerobic respiration
· Anaerobic respiration
Types of respiration:
· Aerobic respiration
· Anaerobic respiration
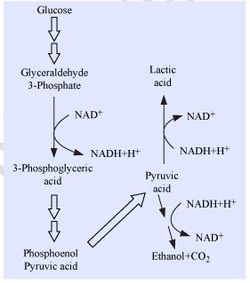
Mechanism of respiration :
· Glycolysis – it is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
· Citric acid cycle / Krebs cycle - Aerobic respiration in mitochondria
· Electron transport system – in the inner membrane of mitochondria
· Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration starts with Glycolysis.
· In aerobic respiration Glycolysis is followed by Citric acid cycle and ETS (both occur in mitochondria).
· In anaerobic respiration Glycolysis is followed by formation of ethyl alcohol / lactic acid in the cytoplasm.
Fermentation :
Incomplete oxidation of pyruvic acid, under anaerobic respiration forms lactic acid/ ethyl alcohol. It occurs in bacteria, yeast and striated muscles.
In yeast fermentation:
o Pyruvic acid → Ethanol + CO2
o Enzymes involved − Pyruvic acid decarboxylase, Alcohol dehydrogenas.
In bacterial fermentation:
o Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid.
o Enzyme involved − Lactate dehydrogenase.
o While doing severe exercise similar reaction occurs in animal muscles in anaerobic conditions.
· Glycolysis – it is common to both aerobic and anaerobic respiration
· Citric acid cycle / Krebs cycle - Aerobic respiration in mitochondria
· Electron transport system – in the inner membrane of mitochondria
· Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration starts with Glycolysis.
· In aerobic respiration Glycolysis is followed by Citric acid cycle and ETS (both occur in mitochondria).
· In anaerobic respiration Glycolysis is followed by formation of ethyl alcohol / lactic acid in the cytoplasm.
Fermentation :
Incomplete oxidation of pyruvic acid, under anaerobic respiration forms lactic acid/ ethyl alcohol. It occurs in bacteria, yeast and striated muscles.
In yeast fermentation:
o Pyruvic acid → Ethanol + CO2
o Enzymes involved − Pyruvic acid decarboxylase, Alcohol dehydrogenas.
In bacterial fermentation:
o Pyruvic acid → Lactic acid.
o Enzyme involved − Lactate dehydrogenase.
o While doing severe exercise similar reaction occurs in animal muscles in anaerobic conditions.
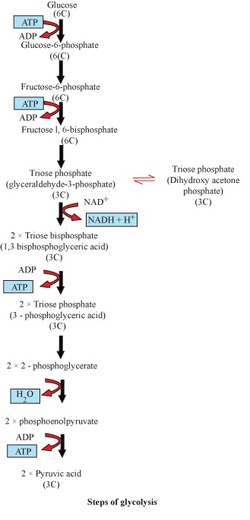
Glycolysis :
Aerobic Respiration
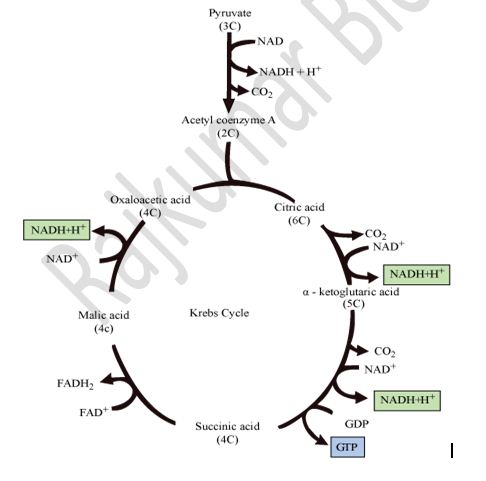
Citric acid cycle / Tricarboxylic acid cycle / Kreb’s cycle:
Formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A
Krebs Cycle/ Tricarboxylic acid cycle / Citric acid cycle:
Overall equation
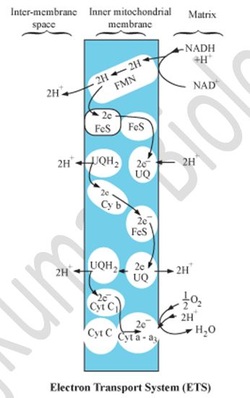
Electron Transport Chain (ETS)
Oxidative Phosphorylation

Respiratory Balance Sheet
Amphibolic Pathway: Involved in both anabolism and catabolism
Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
· RQ is less than 1 for fats.
2 C51 H98 O6 +145 O2 - --> 102CO2 + 98H2O + Energy
RQ = 102 CO2
-------------- = 0.7
145 O2
· RQ is 0.9 for proteins.
· RQ is more than 1 for organic acids.
· RQ is infinite in case of anaerobic resp. because CO2 is evolved but O2 is not consumed
Amphibolic Pathway: Involved in both anabolism and catabolism
Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
· RQ is less than 1 for fats.
2 C51 H98 O6 +145 O2 - --> 102CO2 + 98H2O + Energy
RQ = 102 CO2
-------------- = 0.7
145 O2
· RQ is 0.9 for proteins.
· RQ is more than 1 for organic acids.
· RQ is infinite in case of anaerobic resp. because CO2 is evolved but O2 is not consumed